Pi (letter)
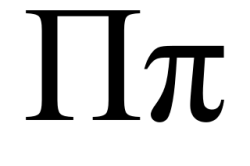
Pi (/ˈpaɪ/; Greek: [pi], uppercase Π, lowercase π) is the sixteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing [p]. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 80. It was derived from the Phoenician letter pe Phoenician pe.svg. Letters that arose from pi include Cyrillic Pe (П, п), Coptic pi (Ⲡ, ⲡ), and Gothic pairthra (
The upper-case letter Π is used as a symbol for:
The product operator in mathematics, indicated with capital pi notation ∏ (in analogy to the use of the capital Sigma Σ as summation symbol).
In textual criticism, Codex Petropolitanus, a 9th-century, uncial codex of the Gospels, now located in St. Petersburg, Russia.
In legal shorthand, it represents a plaintiff.
The osmotic pressure in chemistry. Π=MRT
The lower-case letter π is used as a symbol for:
The mathematical real transcendental (and thus irrational) constant π ≈ 3.1415926535897932384626433832795028841971…, the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter in Euclidean geometry. The letter "π" is the first letter of the Greek words "περιφέρεια" 'periphery' and "περίμετρος" 'perimeter', i.e. the circumference.
The prime-counting function in mathematics.
Homotopy groups in algebraic topology.
Dimensionless parameters constructed using the Buckingham π theorem of dimensional analysis.
The hadron called the pi meson or pion.
Economic profit in microeconomics.
Inflation rate in macroeconomics.
A type of chemical bond in which the P-orbitals overlap, called a pi bond.
The natural projection on the tangent bundle on a manifold.
The unary operation of projection in relational algebra.
In reinforcement learning π denotes policy.
© Symbols.com
