Beta
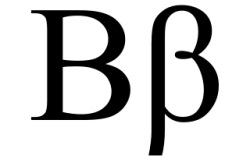
Beta (UK /ˈbiːtə/ or US /ˈbeɪtə/; uppercase Β, lowercase β, or cursive ϐ; Ancient Greek: βῆτα bḗta or Modern Greek: βήτα víta) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 2. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive /b/. In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiodental fricative /v/. Letters that arose from beta include the Roman letter ⟨B⟩ and the Cyrillic letters ⟨Б⟩ and ⟨В⟩.
Like the names of most other Greek letters, the name of beta was adopted from the acrophonic name of the corresponding letter in Phoenician, which was the common Semitic word *bayt ('house'). In Greek, the name was βῆτα bêta, pronounced [bɛ̂ːta] in Ancient Greek. It is spelled βήτα in modern monotonic orthography, and pronounced [ˈvita]. In US English, the name is pronounced /ˈbeɪtə/, while in British English it is pronounced /ˈbiːtə/. Beta in Hindi and Urdu means elder royal son (sometimes also called Beta Ji).
© Symbols.com
